
These thermoplastic polymer materials are high strength, lightweight, exhibit thermal stability, toughness, excellent dimensional stability, and superior electrical insulation properties. Other pertinent characteristics are its transparency, durability, weatherability, outstanding impact/creep resistance, low coefficient of thermal expansion, and recyclability. Special polycarbonate grades are available for use in a variety of colors/tinted, self-extinguishing, anti-static, reflect like a mirror and provide ballistic protection.
Polycarbonates can be processed by:
- Injection molding
- Extrusion
- Structural foam molding
- Vacuum forming
- Blow molding
Examples of typical applications for polycarbonate are:
- Surgical instruments
- Blood reservoirs
- Machinery guards
- Face shields
- Medical imaging devices
- Headlight lenses
- Opto-electronic sensors
- Smart phones
- LED lighting
- Electrical connectors
- 3D printed equipment
- Relay components
- Instrument covers
- Safety helmets
- Semiconductor machinery components
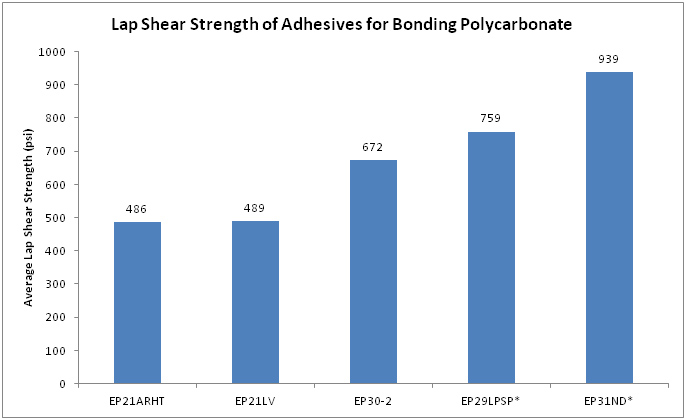
The chart below shows the average lap shear strength in psi for the Master Bond systems noted for bonding polycarbonates.
Considerations for Bonding Polycarbonate
Master Bond produces multiple adhesive systems with unique properties for effectively bonding polycarbonate plastics to each other and to dissimilar surfaces. An important concern is the compatibility of the adhesive compound with polycarbonate plastics. The most significant issue is the possibility of cracking. This phenomenon is known as crazing. The adhesive during cure needs to place minimal stress while still providing strong, robust adhesion.
Master Bond Popular Products
 |
UV10TK40 One component, high viscosity UV curable system. Outstanding optical clarity. Tg 140°C. Enhanced chemical resistance. Superb physical strength properties. Reliable electrical insulator. Withstands 1,000 hours 85°C/85% RH. Serviceable from -60°F to +450°F. |
